STEM Education STEM—Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics—is much more than an educational buzzword. It represents a movement toward critical thinking, innovation, and real-world problem-solving skills. As industries evolve, they increasingly rely on STEM-based knowledge, making these disciplines essential for future generations. However, STEM education isn’t just for budding engineers or scientists; it equips all students with tools to understand and interact with a technology-driven world. This article explores what STEM education entails, its impact on students, its challenges, and the path forward for educators and policymakers.
1. What is STEM Education?
STEM education focuses on four primary disciplines: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, often integrated into a cohesive learning paradigm. Unlike traditional education models that treat each subject as a standalone topic, STEM integrates these disciplines to foster holistic learning. Lessons are frequently project-based, encouraging students to develop their analytical and critical thinking skills.
Example: Instead of teaching algebra in isolation, a STEM approach might involve a real-world scenario, such as designing a bridge, which combines mathematical calculations, physics principles, and engineering design.
2. Why is STEM Education Important?
In today’s world, STEM skills are more relevant than ever. Technology underpins nearly every aspect of modern life, from healthcare advancements to climate science and AI-driven automation. By providing students with a solid foundation in STEM subjects, we prepare them for a world where technology and innovation are vital.
Moreover, STEM education fosters valuable skills beyond the classroom, such as teamwork, creativity, problem-solving, and resilience. These are transferable skills that empower students to navigate challenges across a wide range of professions.
Statistical Insight: According to recent data, jobs in STEM fields are projected to grow by over 10% in the coming decade, significantly faster than the average for other fields. This growth rate indicates a substantial demand for a workforce skilled in these areas.
3. The Benefits of STEM Education
STEM education offers numerous benefits, some of which include:
- Enhanced Critical Thinking: STEM requires students to analyze, evaluate, and make data-driven decisions, which phones critical thinking skills that benefit all areas of life.
- Creativity and Innovation: In a STEM classroom, students are encouraged to experiment, innovate, and learn from failures, which stimulates creativity.
- Preparedness for Future Careers: Many of the highest-paying and fastest-growing careers fall within STEM fields, from data scientists to software engineers. Early exposure to STEM education can guide students toward these opportunities.
- Gender and Diversity Representation: STEM fields have historically been male-dominated, but a concerted effort is being made to include more women and underrepresented groups, creating diverse perspectives that lead to better solutions.
Example Story: A program aimed at increasing female participation in STEM fields saw a significant rise in young women pursuing engineering and computer science majors in college, highlighting the impact of early exposure to these fields.
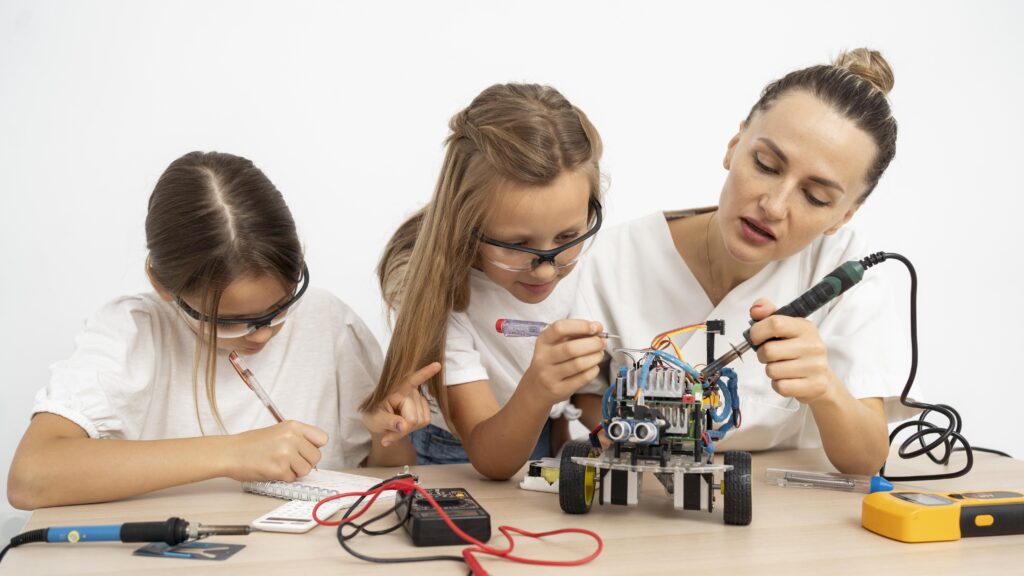
4. Challenges in Implementing STEM Education
Despite its benefits, STEM education faces several challenges:
- Resource Constraints: Implementing a STEM curriculum requires resources such as lab equipment, technology, and trained teachers, which can be costly and difficult to access in underfunded schools.
- Teacher Training and Professional Development: Teachers need specialized training to deliver STEM content effectively. Many educators have strong backgrounds in one area but lack cross-disciplinary expertise.
- Equity in Access: Not all students have the same access to STEM education, particularly in underserved communities. Bridging this gap is essential to create equitable learning opportunities.
- Keeping Up with Rapid Advancements: Technology evolves quickly, often faster than educational curricula can adapt. Schools face the challenge of keeping their programs up-to-date with industry standards.
Case in Point: Many schools in rural areas struggle to keep up with the digital resources needed for STEM, leaving students without access to the same learning tools as their urban counterparts.
5. How to Make STEM Education More Accessible and Effective
For STEM education to succeed, it must be accessible, engaging, and adaptable. Here are some strategies to improve accessibility:
- Invest in Teacher Training: Training educators to teach STEM subjects effectively is one of the most impactful changes schools can make. Professional development programs can help teachers stay up-to-date on the latest educational tools and techniques.
- Develop Engaging Curricula: Project-based learning, where students solve real-world problems, keeps students engaged and makes learning more relevant to their lives.
- Increase Funding for STEM Programs: Allocating resources to fund STEM programs can help underserved schools afford lab equipment, computers, and software.
- Promote Diversity and Inclusion: Initiatives to attract underrepresented groups into STEM can help create a more inclusive and diverse workforce in the future.
6. The Future of STEM Education
The future of STEM education looks promising as more schools, governments, and companies invest in the STEM pipeline. With artificial intelligence, green technology, and data science booming, future jobs will increasingly rely on STEM expertise. Hybrid models incorporating remote learning and digital tools are also likely to become a staple, providing flexible and varied ways for students to engage with STEM subjects.
Looking forward, schools will need to emphasize not just technical skills but also ethical considerations, as fields like AI and biotechnology bring unique ethical challenges. In this light, STEM education will play a pivotal role in developing responsible, thoughtful innovators who can shape technology for the good of society.

Conclusion
STEM education is essential for preparing students to thrive in a technology-driven world. As we continue to face global challenges, from climate change to public health crises, the need for innovative thinkers and problem-solvers has never been greater. By investing in STEM education, we invest in a future workforce equipped not only with technical skills but also with the creativity, resilience, and ethical grounding to make a positive impact.
STEM is more than just four disciplines—it’s a way of thinking, a method of problem-solving, and a pathway to the future. Whether you’re an educator, parent, or policymaker, fostering STEM literacy is a vital step toward a more knowledgeable, capable, and innovative society.

